X-Strategy Services
Categories
Unleashing Profitability: How Mobile App Development Drives High-Growth Businesses
1. Introduction to Mobile App Development and its Significance
The process of developing software applications tailored for mobile platforms, such as smartphones and tablets, is known as mobile app development. Mobile applications have radically changed the ways in which we interact, work, and access information in the current digital era. The importance of developing mobile apps rests in its capacity for offering companies a direct and individualised route to communicate with their customers. Businesses are using mobile applications to increase consumer interaction, boost brand awareness, boost sales, and eventually achieve high growth as smartphones are being used more and more widely throughout the world. With the help of mobile app development, companies can access a huge user base, provide flawless user experiences, and open up new income sources. Businesses may unleash their profitability and maintain an advantage in the current competitive environment by leveraging the potential of mobile apps.
2. The Rising of Mobile Apps in Business
Due to the increasing reliance on smartphones and other mobile devices, mobile applications have become of utmost significance to businesses. Businesses understand the importance of having a strong mobile presence because a sizeable section of the world’s population uses smartphones. Businesses may communicate with their consumers directly and conveniently using mobile applications, which offer individualised experiences, seamless interactions, and beneficial services. They allow for real-time communication, push alerts, and customised marketing efforts, enabling businesses to keep in constant contact with their clients. Because they keep the company constantly on the user’s device, mobile apps help increase brand awareness and customer loyalty. Additionally, mobile applications make it easier to complete transactions quickly, expedite procedures, and gather and analyse data for better decision-making. Mobile applications have evolved into an essential tool for companies looking to survive in the digital age thanks to its capacity to reach a larger audience, enhance customer experiences, and increase revenue.
3. Key Advantages of Mobile App Development for High-Growth Businesses
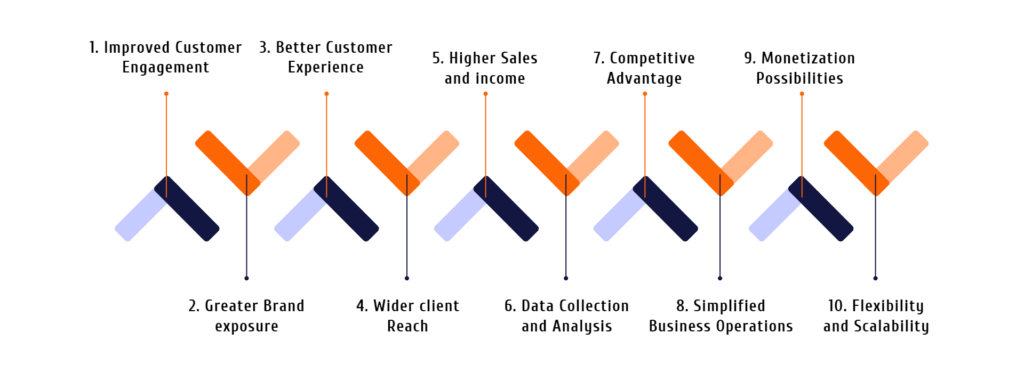
The advantages of developing mobile applications for fast-growing companies can be summed up as follows:
1. Improved Customer Engagement: Mobile applications give businesses a direct and personalised way to communicate with their clients, which boosts conversation, brand loyalty, and client happiness.
2. Greater Brand exposure: The presence of a mobile app on a user’s smartphone acts as a continual reminder of the company and its services, increasing brand exposure.
3. Better Customer Experience: Mobile applications let companies provide seamless user experiences to users with features like tailored suggestions, simple navigation, and user-friendly interfaces, which increases customer satisfaction.
4. Wider client Reach: Mobile applications provide companies access to a worldwide market, allowing them to connect with a larger audience and potentially boosting their client base.
5. Higher Sales and income: Mobile applications may boost sales by giving users a convenient platform to browse and buy goods and services, which boosts income and helps businesses expand.
6. Data Collection and Analysis: Mobile applications make it easier to gather useful user information that can then be examined to learn more about client behaviour, preferences, and trends. Businesses may adjust their offers to fit client expectations thanks to this data-driven strategy, which also helps them make educated decisions.
7. Competitive Advantage: Companies who engage in mobile app development get a competitive edge by providing their clients with distinctive and practical experiences in sectors where mobile applications are not yet extensively utilised.
8. Simplified Business Operations: Mobile apps may simplify internal procedures and activities, enhancing productivity, interaction, and teamwork inside the company.
9. Monetization Possibilities: Businesses may increase their income streams by using mobile applications’ different monetization options, including in-app purchases, subscriptions, advertising, and partnerships.
10. Flexibility and Scalability: Mobile applications can quickly adapt to changing consumer needs and industry trends, enabling high-growth companies to develop and broaden their product offerings.
High-growth companies may take use of these advantages to quicken their growth, boost profitability, and outperform rivals in the mobile-first digital environment.
4. Understanding the Mobile App Development Process
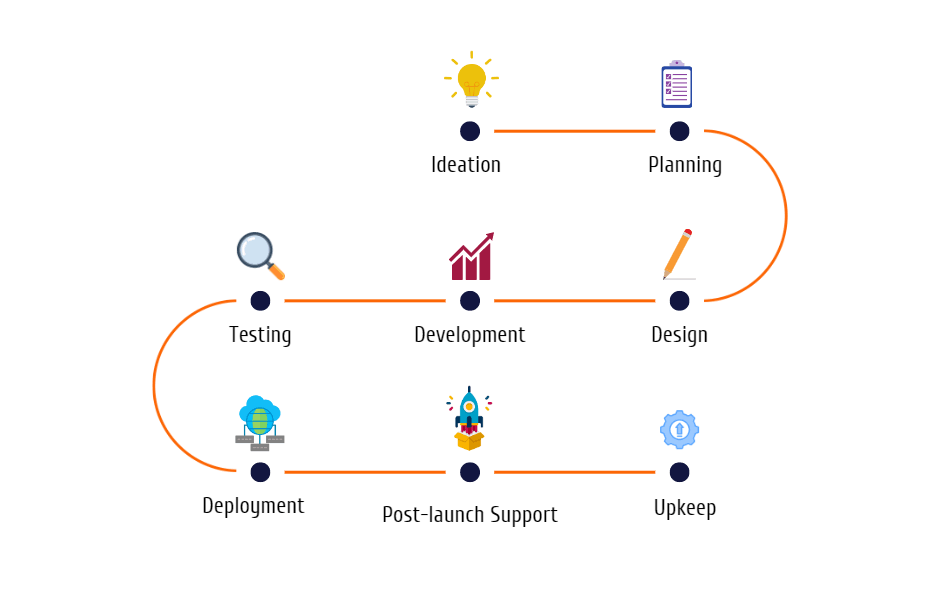
The following key stages are a part of the mobile app development process:
1. Ideation: Outlining the objective, target market, and desired features of the app.
2. Planning: Developing a project blueprint, deciding on objectives, and defining deadlines.
3. Design: Producing the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design for the app to ensure that it is user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
4. Development: This includes front-end and back-end development as well as writing the code and creating the app’s functionality.
5. Testing: Thorough testing is carried out to find and correct any defects, usability flaws, or performance concerns.
6. Deployment: Publishing the app on the targeted app stores (like Apple’s App Store and Google Play Store) or integrating it into the infrastructure of an organisation.
7. Post-launch Support: Tracking the app’s functionality, responding to user comments, and rolling out updates and improvements as required.
8. Upkeep: The app must be regularly updated and maintained to ensure compatibility with new hardware, operating system upgrades, and security patches.
Prioritising user feedback, iterating based on user testing, and following best practises for app speed, security, and user experience are essential throughout the whole mobile app development process.
5. Identifying the Mobile Apps’ Target Market
The following actions are required to determine the target market for mobile apps:
1. Market Research: Learn about the market, business trends, and rivalries by conducting research. Determine the essential characteristics, preferences, and actions of potential app users.
2. User Persona Creation: Create fictitious profiles of the traits, requirements, and objectives of the target audience using user personas based on research findings.
3. User surveys and interviews: Use surveys and interviews to get direct input from potential users and learn about their preferences, problems, and expectations for a mobile app.
4. Analytics and User Data: To acquire insights into user behaviour, demographics, and preferences, analyse data from current platforms, such as websites or social media.
5. Competitor Analysis: Examine the applications and services that rivals provide to pinpoint their target market and find any potential for differentiation.
6. Focus Groups and Beta Testing: To get input on the app’s functionality, usability, and general appeal, hold focus groups or beta tests with a small group of potential users.
7. Iterative Refinement: Keep improving and iterating the app in response to user input to make sure it meets the needs and expectations of the intended audience.
Businesses may better engage and satisfy the demands of their intended users by determining who their target audience is and knowing what they need from their mobile apps. This will increase user adoption, contentment, and success.
6. Using Mobile Apps to Increase Client Retention and Engagement
For businesses looking to forge long-term connections with their clients, utilising mobile applications to boost customer engagement and retention is essential. The following important details describe how mobile apps may be used for this purpose:
1. Personalised Experiences: Businesses may provide customers personalised experiences that are catered to their unique tastes through mobile applications by presenting pertinent material, suggestions, and offers that speak to their needs and interests.
2. Push Notifications: Utilising mobile apps, companies may send push notifications to customers’ devices, informing them of upgrades, specials, brand-new features, or pertinent events. Recurring app usage may be greatly increased, and consumer engagement increased with timely and tailored alerts.
3. Loyalty Programmes and incentives: Mobile applications offer a platform for establishing and managing loyalty programmes that offer special discounts, incentives, or point-accumulation schemes. Businesses may boost client retention and encourage repeat business by rewarding customer loyalty with mobile applications.
4. Seamless Communication Channels: Mobile applications make it easier for businesses and customers to communicate directly, enabling effective customer assistance, the gathering of feedback, and short reaction times. Customer satisfaction and engagement are increased by offering a simple and practical contact route via the app.
5. Gamification and Interactive Features: By using gamification components and interactive features in mobile apps, users may have a more interesting and delightful experience. Long-term involvement can be encouraged by incentives like rewards, challenges, milestones, or interactive material.
6. Social Sharing and Community Building: Mobile applications that support social sharing allow users to post about their adventures, triumphs, or purchases on online forums. This helps to advertise the app and the company while also fostering neighbourhood growth and word-of-mouth advertising.
7. In-App Feedback and Surveys: Through in-app surveys or feedback forms, mobile applications give businesses the chance to get insightful client input. By identifying areas for development and understanding consumer preferences, organisations may better serve their clients.
8. Personalised Recommendations: Mobile applications may provide personalised product or content recommendations based on user behaviour, past purchases, or preferences by using user data and analytics. This degree of personalisation boosts consumer engagement and encourages sales.
By using these tactics, businesses can make the most of mobile applications as a potent tool for retaining and engaging customers, which will eventually result in higher brand loyalty, repeat business, and sustainable growth.
Share your idea or requirement with our experts.
7. Mobile App Monetization Strategies
Mobile app monetization options include making income from the app itself or through supplemental services or features. Here are some salient details outlining various monetization tactics:
1. In-App Advertising: Placing banner, interstitial, or native adverts within the app enables companies to get money from advertisers based on impressions, clicks, or conversions.
2. In-App Purchases: Giving consumers the chance to pay for in-app upgrades, premium content, extra features, or virtual products can bring in money. This tactic is frequently applied in freemium applications.
3. Implementing subscription models that allow users to access premium material, premium features, or exclusive services within the app in exchange for a recurring cost. This tactic may offer a consistent flow of income.
4. The use of a free version of an app with a restricted set of features or material and a paid version with more of those features or content. Users may use the app without having to update thanks to this.
5. Collaboration with Relevant Brands and Companies for Sponsorship and Partnerships: This might open up prospects for money. This can entail advertising their goods or services within the app or via sponsored content.
6. Data Monetization: The app may analyse and sell anonymized user data to third-party advertisers or marketers for the purpose of targeted advertising or market research.
7. Affiliate marketing is the process of integrating affiliate links or referral programmes into an app so that users may get incentives or commissions for recommending friends or customers to partner companies.
8. White Labelling or Licencing: The app may be white-labelled or licenced to other companies or people for a charge if it offers special features or functions.
9. Crowdfunding or Donations: For some applications or services, donation-based business models or crowdfunding platforms can be utilised to collect money from users who support the app’s purpose or objective.
10. E-commerce Integration: By integrating e-commerce features into the app and enabling users to buy things right from the app, businesses may make money through product sales or commissions.
When selecting the best monetization method for their mobile app, businesses should carefully consider their target demographic, app specialty, and user experience. Furthermore, a mix of tactics can be used to increase income potential while preserving a favourable user experience.
8. Comparing Multiple Mobile App Development Technologies and Platforms
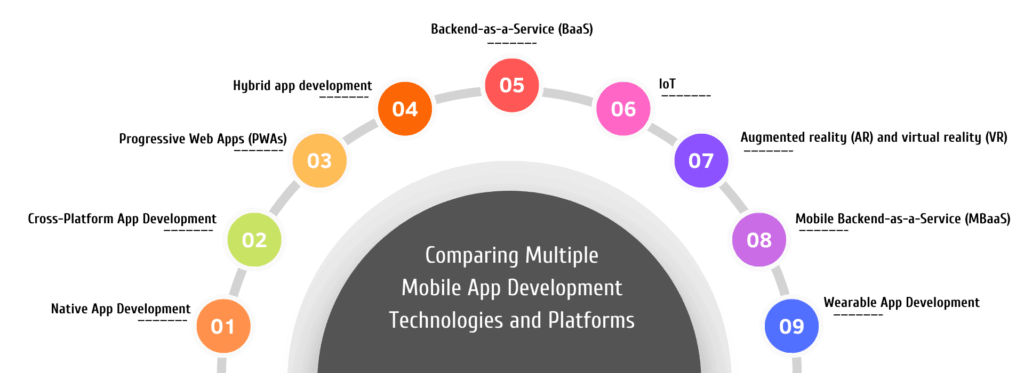
1. Native App Development: Native app development involves creating apps with platform-specific tools and languages, such as Objective-C or Swift for iOS apps and Java or Kotlin for Android apps. Although they need to be developed separately for each platform, native applications provide the best performance and complete access to device features.
2. Cross-Platform App Development: Using frameworks like React Native or Flutter to create apps with a single codebase that can run across several platforms. By enabling developers to create code once and deliver it on both iOS and Android, cross-platform development saves time and effort.
3. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Web-based applications that make use of cutting-edge web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to deliver an app-like experience on various devices. Platform-independent PWAs are accessed through web browsers and do not need to be installed.
4. Hybrid app development: Creating apps using native shells and web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript). Hybrid apps may be installed on several platforms and are created using frameworks like Apache Cordova or Ionic. They provide native performance and code reuse in harmony.
5. Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS): Using the cloud to manage backend features including data storage, user authentication, push notifications, and serverless computing. Examples of such services are Firebase and AWS Amplify. BaaS streamlines backend integration and development for mobile apps.
6. IoT: IoT platforms are used to create apps that communicate with IoT hardware and sensors. Mobile apps may use IoT platforms’ tools, protocols, and APIs to connect and manage a variety of IoT devices, allowing them to be controlled, monitored, and data collected.
7. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR): Investigating ARKit (iOS) and ARCore (Android) for developing AR-enabled apps as well as Unity or Unreal Engine for developing fully immersive VR experiences.
8. Mobile Backend-as-a-Service (MBaaS): Providers like Parse or Kinvey that provide pre-built backend infrastructure, including data storage, user management, and APIs, lessen the burden of backend development on those who create mobile apps.
9. Wearable App Development: Creating apps designed for wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers utilising watchOS (for the Apple Watch) or Wear OS (for smartwatches based on Android).
When selecting the best platform and technology for their mobile app project, companies must take into account their needs, target market, and development resources.
9. Creating Simple and User-Friendly Mobile App Interfaces
The following essential elements go into designing user-friendly and intuitive mobile app interfaces:
1. Simplified Navigation: Design a simple navigation structure that enables users to effortlessly navigate between the app’s many sections or functions.
2. Similar Design Language: To provide a seamless and recognisable user experience throughout the app, maintain a similar design language, including colour palettes, typography, and iconography.
3. Clearly Visible Call-to-Action Buttons: When creating buttons for critical activities like “Submit,” “Save,” or “Purchase,” make sure they stand out and are simple to click.
4. Responsive Layout: Create a responsive layout that changes to accommodate multiple screen sizes and orientations to make sure the app is usable and appealing to users on a variety of devices.
5. Visual Hierarchy: Use the concepts of visual hierarchy to organise and prioritise vital information. For example, use bigger fonts or stronger colours for crucial headings or significant text.
6. Reduced User Input: To improve user experience, employ smart defaults, auto-fill choices, or intelligent form validation to reduce the need for unnecessary user input.
7. Feedback and Error Handling: When users take actions or experience mistakes, provide clear and helpful feedback to them, pointing them in the direction of the intended result and assisting them in troubleshooting problems.
8. Intuitive movements: To allow natural and fluid interactions inside the app, use intuitive movements like swiping, pinching, or tapping.
9. Visual Cues and Affordances: Use visual cues and affordances to direct users and give feedback on the current state or anticipated activities, such as button statuses or progress indications.
10. User Testing and Iteration: To ensure ongoing improvement of the user interface, conduct user testing to get input on the usability of the app and iterate the design based on user insights.
Designers may produce user-friendly, intuitive, and enhanced user experiences for mobile apps by concentrating on these factors, which will increase user engagement and happiness.
10. Tips for Hiring a Mobile App Development Team or Company
Think about the following advice before selecting a mobile app development team or mobile app development company:
1. identify Your Project Scope: To successfully interact with possible teams or agencies, clearly identify your project requirements, goals, and timetable.
2. Evaluate Relevant expertise: Check the portfolio of the team or agency to see whether they have expertise creating mobile applications that meet the specifications of your project.
3. Verify References and Reviews: Ask for references and check customer reviews to see how satisfied they were with the team’s or agency’s performance.
4. Technical Expertise: Assess the group’s or organization’s technical abilities, including their command of the necessary platforms, frameworks, and programming languages.
5. Communication and Collaboration: Evaluate their manner of communication, responsiveness, and capacity for productive collaboration throughout the development process.
6. Project Management methodology: To guarantee effective collaboration, accurate tracking of progress, and on-time delivery, find out about their project management methodology and tools.
7. Quality Assurance and Testing: Verify their procedures for quality assurance and testing to guarantee that the software will be rigorously examined for usability, functionality, and security.
8. Cost and Budget: Talk with the team or agency about the project’s budget and pricing models to guarantee alignment and prevent any surprises later in the development process.
9. Maintenance and Support: Enquire about any post-launch maintenance plans, future upgrades, or app improvements.
10. Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA): Take into consideration signing an NDA if necessary to safeguard your app concept and any private information disclosed throughout the recruiting process.
By taking into account these suggestions, you may choose wisely when selecting a mobile app development team or agency, laying the groundwork for an effective partnership and the production of a high-quality mobile app.
11. Conclusion
In conclusion, the creation of mobile apps has become a key driver of rapid corporate growth. Businesses that use mobile applications may reap a variety of benefits as a result of the rising use of smartphones and the transition to mobile-first experiences. Mobile applications increase consumer interaction, offer individualised experiences, and raise brand awareness. They provide efficient processes, effective communication channels, and insightful data for deft decision-making. Additionally, through in-app purchases, subscriptions, advertising, and partnerships, mobile applications provide additional income sources. Businesses may remain ahead of the competition, generate a clear competitive edge, and achieve long-term profitability by adopting mobile app development. Mobile app development is a revolutionary force that propels high-growth enterprises towards success in the digital era because it enables them to personally engage with consumers, provide amazing user experiences, and take advantage of the mobile revolution.






